Peripheral Artery Disease (PAD)
What is Peripheral Artery Disease (PAD)?
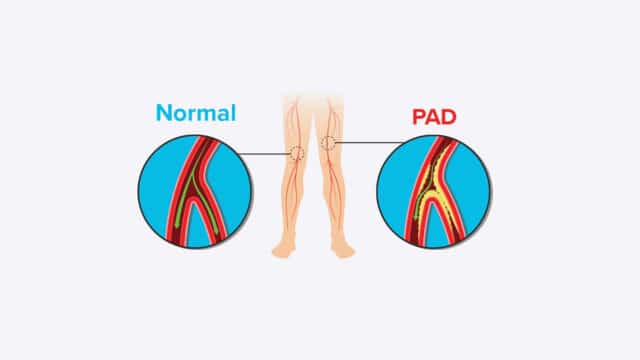
Peripheral Artery Disease (PAD) is a condition that develops when the arteries that supply blood to the internal organs, arms and legs become completely or partially blocked. This blockage is caused by fatty plaque deposits that harden arteries, called atherosclerosis, and greatly reduces blood flow.
PAD affects nearly 10 million people in the United States, especially those over 65 years of age. PAD increases the risks of hard-to-heal wounds and associated lower-limb amputations by negatively impacting circulation and reducing blood flow to and from the legs.
What Causes PAD?
PAD develops when plaque and fatty deposits build-up and block the peripheral arteries, those arteries delivering blood farther away from the heart. There are many factors that contribute to these fatty deposits. However, lifestyle choices such as diet and exercise have a large impact on the health of your arteries.
Risk Factors for PAD Include:
- Smoking
- High cholesterol
- High blood pressure
- Diabetes
- Heart disease
- Obesity
- Family history of artery disease
- Age above 65 years
Common Symptoms of PAD
Do not dismiss leg pain as part of growing old. Seek medical care and screening for PAD if you have these symptoms:
- Pain or cramps in the back of your leg while walking or exercising. These pains or cramps go away when the walking or exercising stops.
- Pain in the feet or legs while resting or that wake you from sleep.
- Decreased or no hair growth on the feet or legs.
- Lower legs and feet that are cool to touch or that have shiny skin.
- Legs and feet that appear pale when raised and blueish/purplish when hanging down.
- Weak or absent pulses in the legs or feet.
- Numbness or tingling in the feet and legs.
- A sore or wound on your toes, legs or feet that does not heal.
Testing for PAD
Your Wound Care Center can perform non-invasive tests to diagnose and accurately treat PAD.
Ankle-Brachial Index (ABI)
An ABI test is painless and easy. Your medical technician will take your blood pressure in your ankle and your arm and then compare the two readings. An ABI can help diagnose PAD, but it cannot identify which arteries are narrowed or blocked.
Doppler Ultrasound Test
If your blood pressure reading indicate a blockage, an ultrasound may be done to see which artery or arteries are blocked. This painless procedure uses high frequency sound waves to create an image of your internal blood vessels.
Treatment and Prevention of Peripheral Artery Disease:
- Diet low in saturated fats
- Weight management
- Regular, moderate exercise or a supervised exercise training program
- Medicine or procedures ordered by your healthcare provider
- Stop smoking
- Wound care ordered by your healthcare provider
Specialized wound care can reduce healing times, increase healing rates and significantly lower amputation risks.
If you or someone you care for is at risk for PAD and has a wound that is not healing, find a Center near you today.