This peer-reviewed case series addresses the clinical challenge of managing chronic, nonhealing wounds using advanced modalities – specifically, bioactive skin allografts (BSAs). BSAs are cellular and/or tissue-based products (CTPs) designed to promote tissue repair by supporting angioenesis, cellular proliferation, and immune modulation. A key innovation discussed is the use of bacterial fluorescence imaging (FL-imaging), a…
Learn More
As part of the People-first, Patient-centered focus, Healogics® is dedicated to continuously improving patient outcomes. A process was developed to identify and evaluate critical topics to determine the levers which would result in reducing unwarranted clinical variability across our organization and improve Comprehensive Healing Rates (CHR) amongst our patients. Four levers were identified utilizing the…
Learn More
Healogics is the nation’s largest world-class wound care provider, delivering compassionate care to more than 300,000 patients each year. Our focus is on providing the highest level of integrated wound care management throughout the continuum of care: post-acute, outpatient and inpatient.
Learn More
In the second installment of the use of modalities in wound care white paper, we will review the use of hyperbaric oxygen (HBO therapy) as a lever for reducing unwarranted clinical variability.
Learn More
In this white paper, we will review the use of modalities as a lever for reducing unwarranted clinical variability. This is the fourth in a series of white papers that have tried to provide evidence and clinical guidance for providers managing complex wound patients. As in all previous white papers, the literature has been reviewed, the data has been updated and refreshed using a 2019 research database from Healogics and recommendations have been formulated for consideration.
Learn More
The COVID-19 pandemic provides direct evidence of why wound care is an essential service. Along with many other service lines, wound care has seen a decline in visits despite being designated as an essential service and the adoption of telemedical options. There have been several recently published articles that report significant increases in major limb amputations during the pandemic compared with matched time frames from pre-COVID-19 data.
In this article, Dr. Ennis briefly describes the findings and compares them to his own University’s data, with the goal of ensuring patients are scheduled and evaluated during these complicated times.
Learn More
As part of our ongoing research aimed at minimizing unwarranted clinical variability and improving healing rates, we have already reported on visit frequency and the impact of wounds that fail to heal on a normal trajectory. In this report, we describe the impact on healing when patients either cancel visits, or completely quit their treatment plan.
Learn More
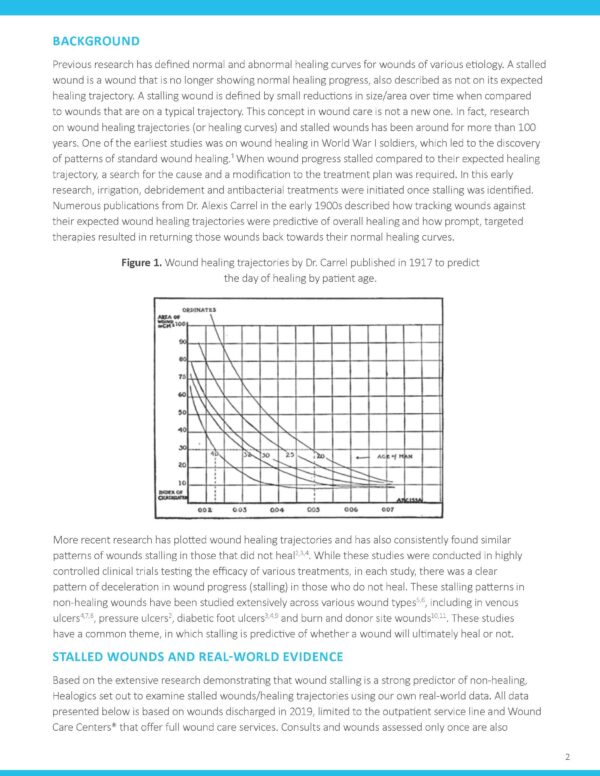
Recently, we introduced four levers that could improve our patient outcomes. These levers included frequent patient visits, the prevention of stalled wounds, improving patient engagement and utilizing advanced modalities. The focus of this paper will be on the evidence and research supporting the key lever of preventing stalled wounds in driving better patient outcomes.
Learn More
Healogics developed a process to identify and evaluate critical topics to determine the levers which would result in reducing unwarranted clinical variability across our organization and improve Comprehensive Healing Rates (CHR) amongst our patients.
Learn More
Speaking from four separate rooms in four different corners of the world, William Ennis, Desmond Bell, Michael Edmonds, and William Li expounded over zoom on the myriad ways in which COVID-19 had impacted multidisciplinary wound care, both in terms of the disruption the pandemic had caused to their daily practices, and how the echoes of this disruption would ripple into the future. They also touched on the interrelationship between diabetes and COVID-19, questioning what the downstream effects will be in the vulnerable diabetic population.
Learn More